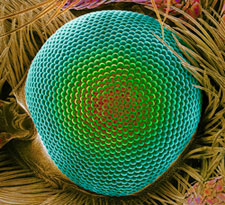
 Anti-reflective film based on moth eyes increases efficiency of photovoltaics The eyes of moths, which allow them to see well at night, are also covered with a water-repellent, antireflective coating that makes their eyes among the least reflective surfaces in nature and helps them hide from predators in the dark. Mimicking the moth eye’s microstructure, a team of researchers in Japan has created a new film, suitable for mass-production, for covering solar cells that can cut down on the amount of reflected light and help capture more power from the sun.
Anti-reflective film based on moth eyes increases efficiency of photovoltaics The eyes of moths, which allow them to see well at night, are also covered with a water-repellent, antireflective coating that makes their eyes among the least reflective surfaces in nature and helps them hide from predators in the dark. Mimicking the moth eye’s microstructure, a team of researchers in Japan has created a new film, suitable for mass-production, for covering solar cells that can cut down on the amount of reflected light and help capture more power from the sun.
In a paper appearing in Energy Express, a bi-monthly supplement to Optics Express, the open-access journal published by the Optical Society (OSA), the team describes how this film improves the performance of photovoltaic modules in laboratory and field experiments, and they calculate how the anti-reflection film would improve the yearly performance of solar cells deployed over large areas in either Tokyo, Japan or Phoenix, Ariz. “Surface reflections are an essential loss for any type of photovoltaic module, and ultimately low reflections are desired,” says Noboru Yamada, a scientist at Nagaoka University of Technology Japan, who led the research with colleagues at Mitsubishi Rayon Co. Ltd. and Tokyo Metropolitan University.
The team chose to look at the effect of deploying this antireflective moth-eye film on solar cells in Phoenix and Tokyo because Phoenix is a “sunbelt” city, with high annual amount of direct sunlight, while Tokyo is well outside the sunbelt region with a high fraction of diffuse solar radiation.They estimate that the films would improve the annual efficiency of solar cells by 6 percent in Phoenix and by 5 percent in Tokyo. Yamada and his colleagues found the inspiration for this new technology a few years ago after they began looking for a broad-wavelength and omnidirectional antireflective structure in nature. The eyes of the moth were the best they found. The team is now working on improving the durability of the film and optimizing it for many different types of solar cells. They also believe the film could be applied as an anti-reflection coating to windows and computer displays.
Habitat for Humanity Partners to Create Its First Eco-Tourism Village in the World
Project will make Indonesian history, culture accessible to international visitors
 YOGYAKARTA, Indonesia -Habitat for Humanity Indonesia today announced it is partnering with Asia Pulp & Paper (APP) to create Habitat’s first eco-tourism village of more than 420 homes and guest accommodations near some of Indonesia’s most picturesque ancient temples.
YOGYAKARTA, Indonesia -Habitat for Humanity Indonesia today announced it is partnering with Asia Pulp & Paper (APP) to create Habitat’s first eco-tourism village of more than 420 homes and guest accommodations near some of Indonesia’s most picturesque ancient temples.
“This unique program not only improves housing for most of the community, it also allows Soran villagers to economically benefit from the art and culture they have preserved for centuries, and to share it with the world.”
The development will take place in the village of Soran, located near the famous Prambanan Temple, a UNESCO World Heritage Site built around 850 AD. The village is also located near Mount Merapi, the nation’s most famous volcano, which erupted last year. Read more in
ECOTOURISM








